
8 Jan 2026
A Paradigm Shift in Modern Farming
As the global community intensifies its efforts to combat climate change, the agricultural sector is undergoing a profound transformation. No longer seen merely as a source of food production, farmland is now being recognized as one of our most potent tools for climate mitigation. This transition is led by Carbon Farming, a revolutionary agricultural approach focused on capturing atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) and storing it securely within the soil and vegetation.
At GlobalEsco, we provide the cutting-edge technologies necessary to turn this environmental necessity into a productive and profitable reality. Central to this mission is Biochar, a technology that doesn't just improve soil, but fundamentally changes the carbon cycle of the farm.
Understanding Carbon Farming: Practices and Principles
Carbon Farming refers to a suite of management practices designed to increase the rate at which CO2 is removed from the atmosphere and converted into plant material and soil organic matter. By enhancing the soil’s natural "carbon sink" capacity, farmers can build land that is more resilient, fertile, and ecologically balanced.
Core Carbon Farming Methods:
Agroforestry: The strategic integration of trees and shrubs with crops and livestock to capture carbon in woody biomass and deep soil layers.
Cover Cropping: Maintaining living roots in the soil year-round to protect the surface from erosion and continuously feed organic matter back into the earth.
Reduced Tillage / No-Till Farming: Minimizing soil disturbance to prevent the oxidation of organic matter, ensuring that stored carbon remains trapped underground.
Rotational Grazing: Managing livestock movement to allow pastures to recover, which stimulates deep root growth and increases carbon sequestration.
Organic Amendments: The application of compost and biochar to rapidly boost the soil’s stable carbon content and microbial life.
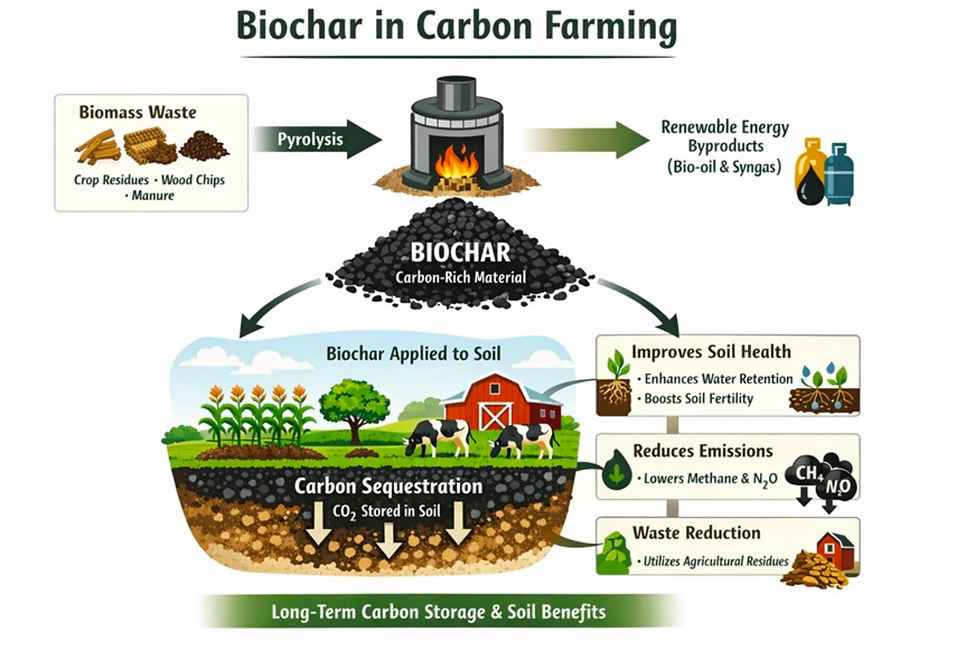
Biochar: The Permanent Carbon Solution
While many organic materials eventually decompose and release their carbon back into the atmosphere, Biochar is different. It is a stable, carbon-rich material produced via pyrolysis, the heating of organic biomass (such as wood chips, crop residues, or manure) in a low-oxygen environment at temperatures between 300°C and 800°C.
Unlike traditional combustion (burning), which releases CO2, pyrolysis "locks" the carbon into a solid, stable form. This process also creates valuable renewable energy byproducts, including bio-oil and syngas, which can be used to power the pyrolysis unit or other farm operations.
Key Characteristics of Biochar:
Extreme Stability: The carbon in biochar is highly resistant to microbial breakdown, allowing it to remain in the soil for hundreds or even thousands of years.
Unrivaled Porosity: Biochar possesses a massive surface area. A single gram of high-quality biochar can have a surface area of up to 500 m², the equivalent of two tennis courts!
Functional Chemistry: The surface of biochar is covered in functional groups that allow it to bind to nutrients and moisture, acting as a long-term reservoir for the plant.
The Soil "Battery": How Biochar Boosts Productivity
Biochar functions as a permanent infrastructure for your soil. It is often referred to as a "soil battery" because of its ability to store and release energy, water, and nutrients when the crop needs them most.

1. Water Retention and Drought Resilience
The porous structure of biochar acts like a microscopic sponge. In sandy soils, it provides the cohesion needed to hold onto water that would otherwise drain away. In heavy clay soils, it improves drainage and aeration. This can lead to an irrigation saving of up to 50%, providing a critical safety net during dry seasons.
2. Nutrient Management and Slow Release
One of biochar's most significant roles is as a regulator for nutrients like Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K). By holding these ions in its pores, biochar prevents "leaching", the process where expensive fertilizers wash away into groundwater. Instead, it provides a slow-release mechanism that matches the plant's growth cycle, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizer inputs by 20–40%.
3. Denitrification and Emission Reduction
Biochar helps mitigate the release of potent greenhouse gases like nitrous oxide (N2) and methane (CH4) from the soil. Its unique "micro-caves" create anaerobic zones that support beneficial denitrifying microbes, which convert harmful nitrates into harmless atmospheric nitrogen (N2).
Professional Application: The GlobalEsco Protocol
To achieve the best results, biochar application must be handled with professional precision. GlobalEsco recommends the following implementation strategy:
Dosage: A standard effective rate is 200–500g per m² (approximately 1 cubic meter per stremma).
Pre-Activation ("Charging"): We strongly recommend mixing biochar with compost or liquid organic fertilizer for 2–4 weeks before application. This ensures the biochar is fully "charged" with nutrients and microbes before it enters the soil.
Incorporation: For field crops, biochar should be tilled into the soil at a depth of 10–30 cm. For permanent crops like trees or vines, it can be applied in the root zone during planting or through specialized soil injection.

The Economic Advantage:
Carbon Credits and Valorization
Beyond the physical benefits to the soil, biochar offers a direct financial return through the Circular Economy. By transforming agricultural waste into a high-value soil amendment, farmers solve two problems at once: waste management and soil degradation.
Furthermore, because biochar represents a permanent Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR) technology, it qualifies for high-value carbon credits. In GlobalEsco we assist our clients in documenting these sequestration rates, allowing them to tap into international carbon markets and generate additional revenue streams.
Conclusion: Building a Resilient Agricultural Legacy
The future of agriculture lies in the harmony of technology and nature. By adopting Carbon Farming practices and integrating Biochar technology, producers can ensure their land remains productive for generations to come. At GlobalEsco, we don't just sell technology; we build the foundations for a sustainable, resilient, and profitable agricultural future.
Contact GlobalEsco today, to discuss how our pyrolysis & biochar systems
can be tailored to your specific crops and climate.

